


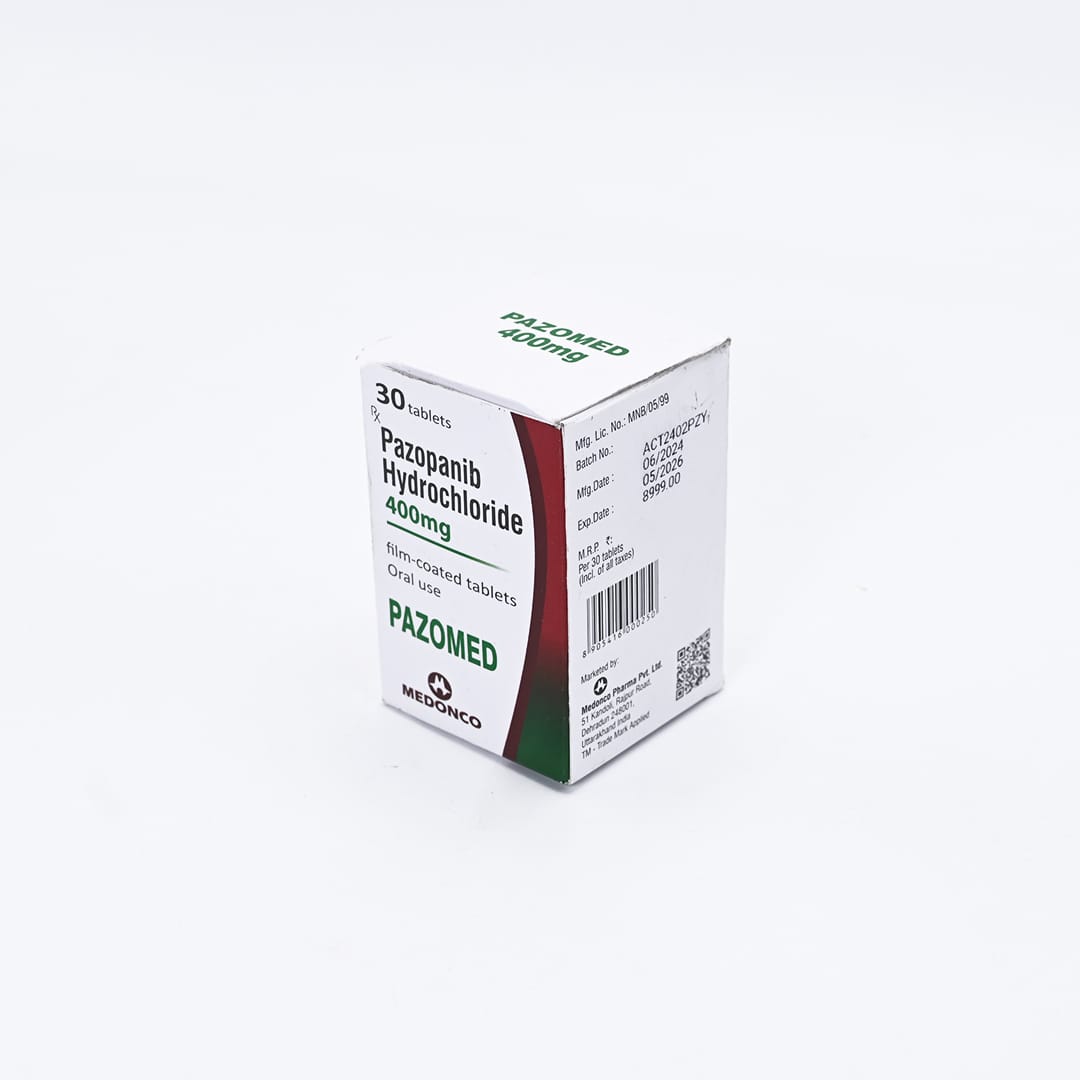

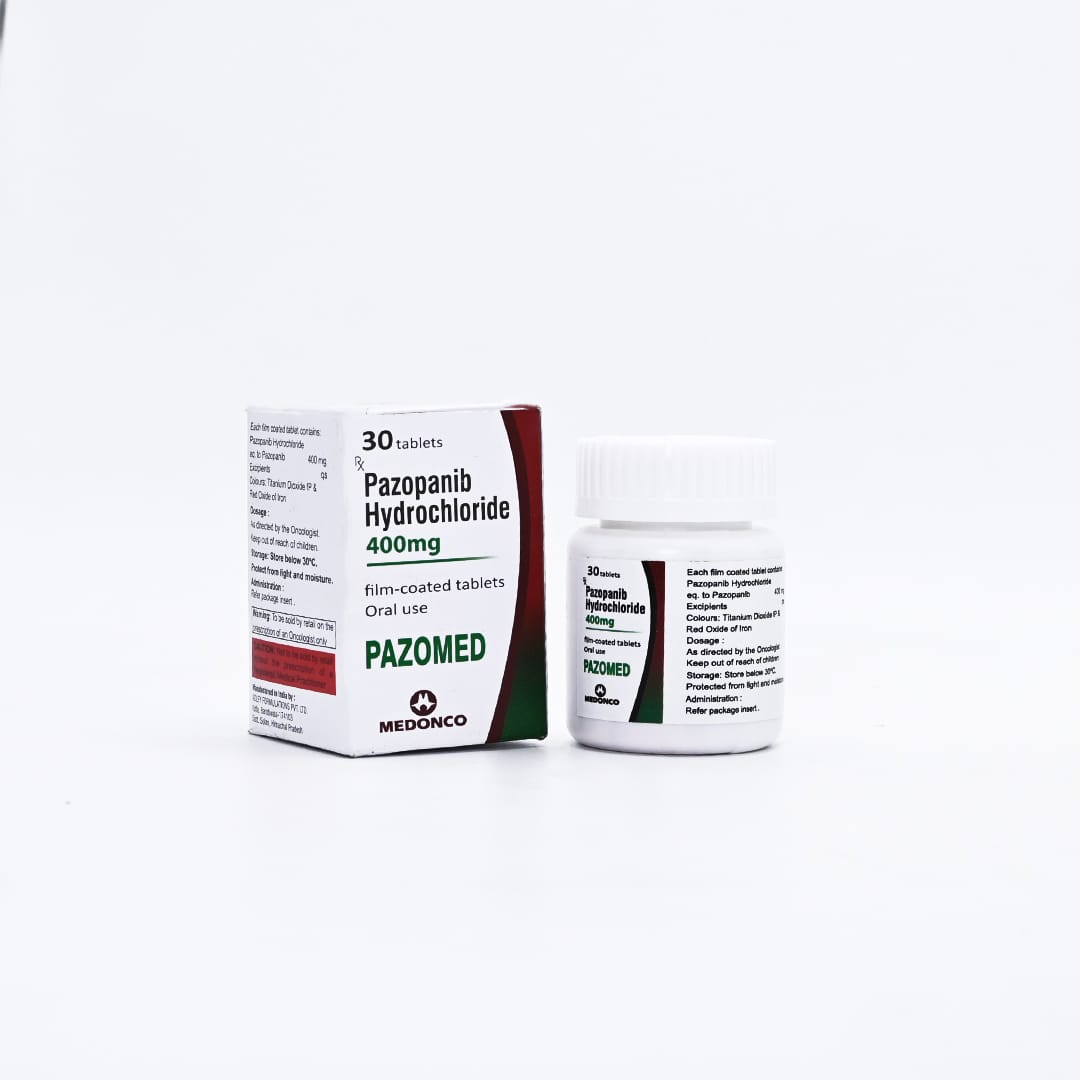
PAZOMED 400MG
Pazopanib Hydrochloride 400mg
Net Qty- 30 Tablets
Shelf-Life- 2 Years
Pazopanib Hydrochloride 400mg is an oral Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) targeting multiple receptors involved in tumor growth and angiogenesis. It is widely used in oncology, particularly in kidney and soft tissue cancers.
USE
Pazopanib is FDA-approved for:
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC):
- First-line treatment or for patients with prior cytokine therapy.
Advanced Soft Tissue Sarcoma (STS):
- Specifically for patients who have received prior chemotherapy.
Mechanism
of Action
Pazopanib inhibits multiple Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) associated with angiogenesis and tumor proliferation, including:
- VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3 (vascular endothelial growth factor receptors): Blocks angiogenesis.
- PDGFR-α, PDGFR-β (platelet-derived growth factor receptors): Disrupts stromal support for tumors.
- c-KIT, FGFR: Inhibits oncogenic signaling pathways.
This action limits blood supply to the tumor and reduces its growth.
Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosing:
400-800 mg once daily, taken orally.
RCC: Typically 800 mg/day.
STS: 800 mg/day.
Administration Instructions:
Take on an empty stomach (1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal).
Swallow tablets whole; do not crush or chew, as it may alter drug absorption.
Dose Modifications:
Adjust doses in increments of 200 mg based on tolerance and side effects.
Max dose: 800 mg/day.
Common Side Effects
Frequent (>20%):
- Hypertension:
- A common side effect; requires regular monitoring and antihypertensive therapy if necessary.
- Diarrhea:
- Manageable with anti-diarrheal agents like loperamide.
- Nausea and Vomiting.
- Fatigue:
- Significant but manageable with rest and energy conservation techniques.
- Hair Color Changes:
- Hypopigmentation of hair is harmless but noticeable.
Liver Toxicity:
- Elevated liver enzymes (ALT, AST) and bilirubin are common and may require dose adjustments.
Severe or Rare Side Effects
Hepatotoxicity:
- Rare cases of severe liver damage. Regular liver function tests are critical.
Cardiotoxicity:
- Can cause QT prolongation; ECG monitoring is recommended for at-risk patients.
Hemorrhagic Events:
- Rare, but monitor for signs of bleeding.
Proteinuria (Excess Protein in Urine):
- Regular urinalysis is advised.
Hypothyroidism:
- Monitor thyroid function regularly during treatment.
Monitoring and Precautions
Baseline Assessments:
- Liver Function Tests (LFTs): ALT, AST, bilirubin.
- Blood Pressure: Control pre-existing hypertension before starting pazopanib.
- Thyroid Function: Baseline and periodic monitoring.
During Treatment:
- LFTs: Weekly during the first 8 weeks, then periodically.
- Blood Pressure: Measure regularly; consider antihypertensive therapy for persistent hypertension.
- ECG: Monitor QT interval in patients with cardiac risk factors.
- Urinalysis: Monitor for proteinuria.
Precautions:
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Contraindicated due to potential fetal harm.
- Contraception: Use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose.
Drug Interactions
CYP3A4 Inhibitors:
- Drugs like ketoconazole, erythromycin, or grapefruit juice increase pazopanib levels, raising toxicity risk.
CYP3A4 Inducers:
- Drugs like rifampin or phenytoin decrease pazopanib levels, reducing efficacy.
QT-Prolonging Agents:
- Avoid combining with drugs that prolong the QT interval (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol).
Clinical Effectiveness
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC):
- COMPARZ Trial: Pazopanib was shown to have similar efficacy to sunitinib in prolonging progression-free survival (PFS) but had a more favorable side effect profile, especially in terms of fatigue and quality of life.
Soft Tissue Sarcoma (STS):
- Proven to improve PFS in patients with advanced STS who have failed prior chemotherapy.
Tips for Patients
Practical Tips for Patients
Adherence:
- Emphasize taking the medication on an empty stomach for optimal absorption.
Blood Pressure Management:
- Encourage regular home monitoring and lifestyle adjustments (e.g., low-salt diet).
Hydration and Diarrhea:
- Advise staying hydrated and using anti-diarrheal medication if necessary.
Report Symptoms:
- Early reporting of jaundice, severe fatigue, or chest pain can prevent complications.