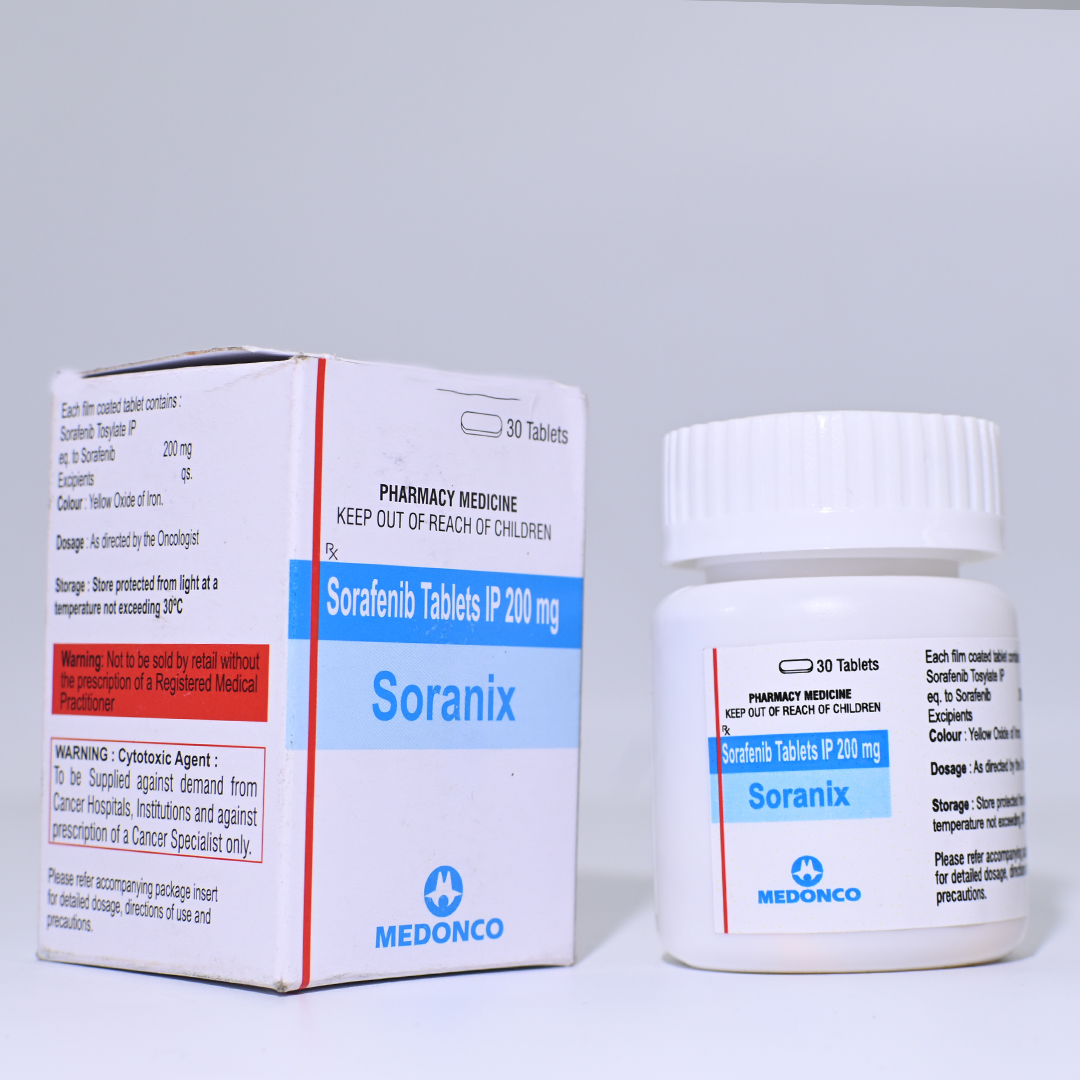
SORANIX


SORANIX 200MG
Sorafenib 200mg Tab
Net Qty- 30 Tablet
Shelf-Life- 2 Years
Soranix (Sorafenib 200mg Tablet) is an oral multi-kinase inhibitor used in cancer therapy. It targets tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis pathways, making it effective in specific types of advanced cancers.
USE
Sorafenib is used for treating specific cancers, particularly when they are advanced or metastatic:
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC):
Effective for primary liver cancer, especially when surgical or locoregional therapies are not suitable. - Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC):
For advanced kidney cancer in patients who have failed prior therapies or are ineligible for surgery. - Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (DTC):
For progressive, radioactive iodine-refractory cases of thyroid cancer.
Mechanism
of Action
Sorafenib inhibits multiple signaling pathways involved in tumor growth and angiogenesis:
Angiogenesis Inhibition:
- Targets VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, and PDGFR-β, reducing blood vessel formation.
Tumor Cell Proliferation Inhibition:
- Blocks RAF kinases (CRAF, BRAF) and other signaling molecules, disrupting the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway.
This dual-action mechanism makes sorafenib effective in slowing tumor growth and spread.
Administration
Standard Dosage:
- 400 mg (2 tablets) twice daily, taken approximately 12 hours apart.
Administration Guidelines:
- Take on an empty stomach (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal).
- Swallow tablets whole with water.
Dose Modifications:
- Dose reductions are required for managing side effects, starting at 400 mg once daily, then to 200 mg once daily if necessary.
Common Side Effects
Frequent (>20%):
- Hand-Foot Syndrome (HFS):
- Redness, pain, or peeling of palms and soles.
- Hypertension:
- Regular monitoring is critical.
- Diarrhea:
- Common but manageable with anti-diarrheal agents like loperamide.
- Fatigue and Asthenia:
- Dose interruptions or reductions may help.
- Rash and Skin Reactions:
- Often seen in the early treatment phase.
Mild to Moderate:
- Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, weight loss, and alopecia.
Serious or Rare Side Effects
- Hepatotoxicity:
- Elevated liver enzymes or severe liver injury. Monitor ALT/AST and bilirubin regularly.
- Cardiac Events:
- Rare but serious ischemic events; ECG and cardiac monitoring may be necessary in at-risk patients.
- Hemorrhagic Events:
- Increased risk of bleeding; avoid in patients with high bleeding risk.
- GI Perforation:
- A rare but severe complication requiring immediate medical attention.
- Hypocalcemia:
- Monitor serum calcium levels during treatment.
Monitoring and Precautions
Baseline and Regular Monitoring:
- Liver Function Tests (LFTs):
- Baseline, every 2 weeks during the first 2 months, and periodically thereafter.
- Blood Pressure:
- Check weekly during the first 6 weeks, then periodically.
- Renal Function:
- Especially in patients with pre-existing renal impairment.
- Electrolytes:
- Monitor potassium, calcium, and phosphate levels.
Precautions:
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
- Contraindicated due to teratogenic effects.
- Contraception:
- Use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 2 weeks after discontinuation.
- Surgical Wounds:
- Discontinue 2 weeks prior to surgery and resume after adequate wound healing.
Drug Interactions
- CYP3A4 Inducers:
- Rifampin, carbamazepine: May reduce sorafenib levels and efficacy.
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors:
- Ketoconazole, erythromycin: May increase sorafenib toxicity.
- Anticoagulants:
- Monitor closely for increased bleeding risk when used with warfarin.
- QT-Prolonging Drugs:
- Avoid co-administration to minimize the risk of cardiac arrhythmias.
Clinical Effectiveness
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC):
- SHARP Trial: Sorafenib significantly improved overall survival (OS) compared to placebo in patients with advanced HCC.
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC):
- Shown to improve progression-free survival (PFS) in cytokine-refractory metastatic RCC.
Thyroid Cancer:
- Improves PFS in radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid carcinoma.
Managing Side Effects
Hand-Foot Syndrome (HFS):
- Use emollients and avoid friction or heat exposure.
- Dose reduce if severe.
Diarrhea:
- Treat with loperamide and maintain hydration.
Hypertension:
- Initiate antihypertensive therapy (ACE inhibitors or calcium channel blockers).
Skin Reactions:
- Use mild corticosteroid creams or antihistamines for symptomatic relief.
Fatigue:
- Encourage rest, light activity, and dose adjustments if needed.
Tips for Patients
- Adherence:
- Take consistently on an empty stomach for optimal efficacy.
- Report Symptoms Early:
- Jaundice, chest pain, or severe diarrhea should prompt immediate consultation.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Avoid high-fat meals, alcohol, and activities that risk skin irritation.