SUNITEX
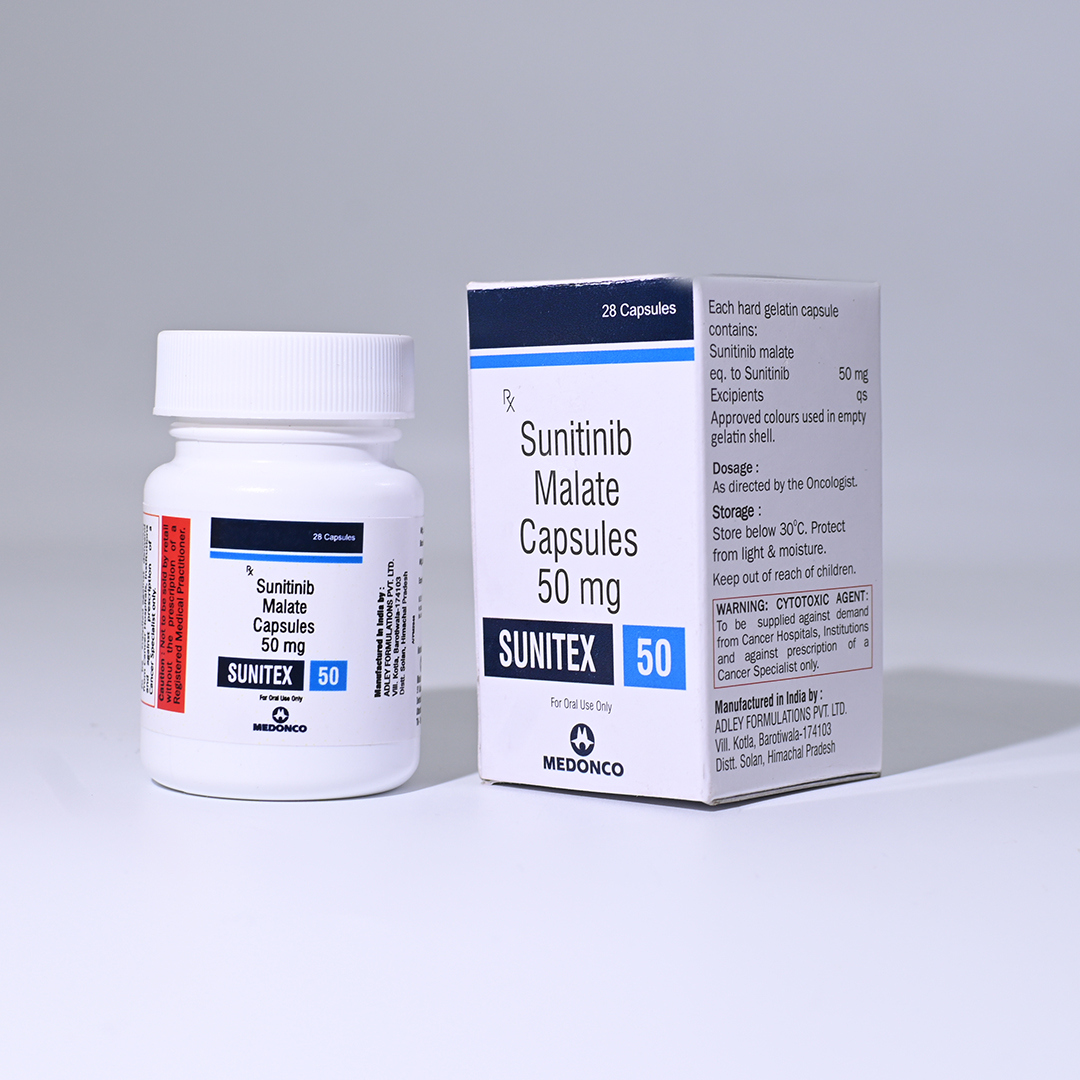
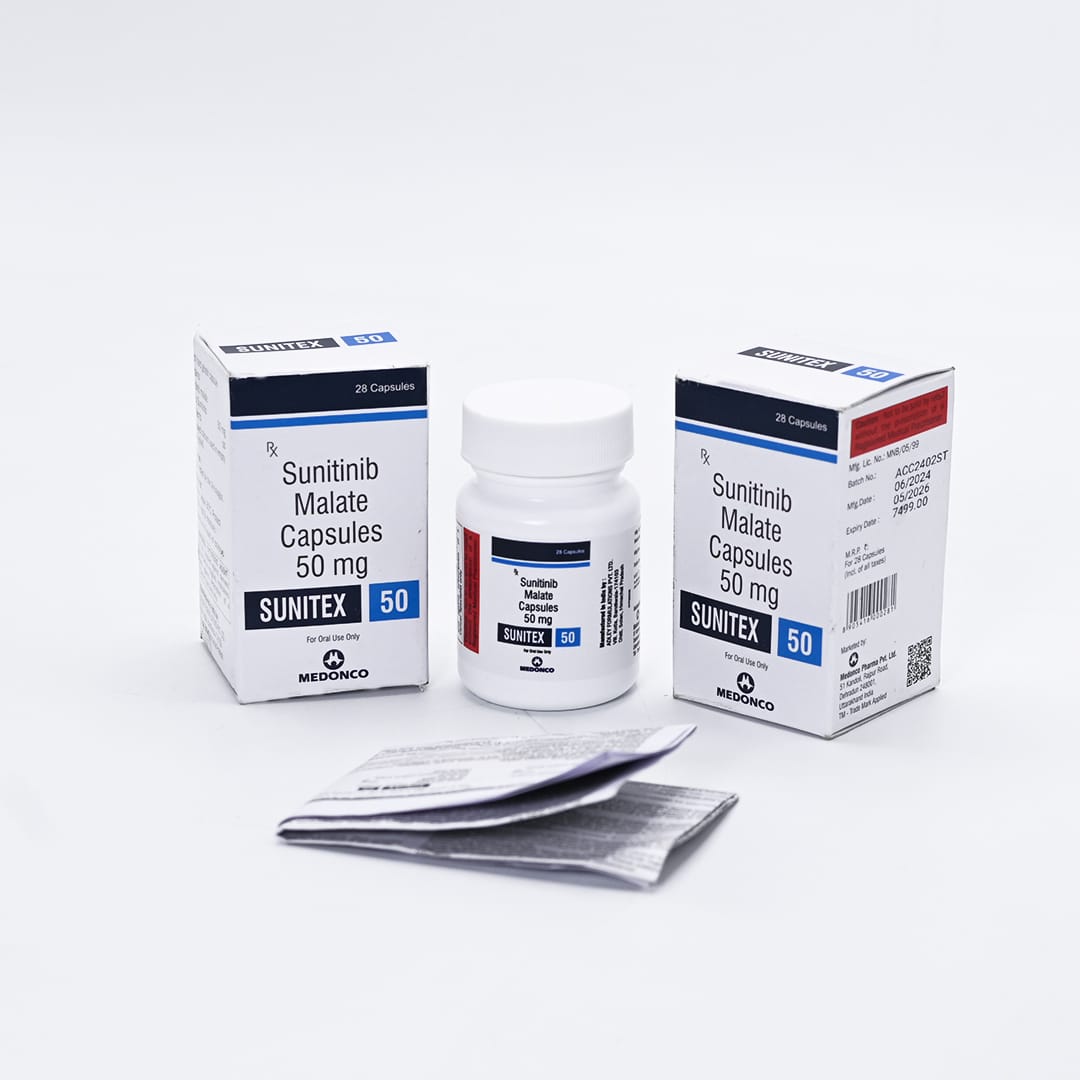
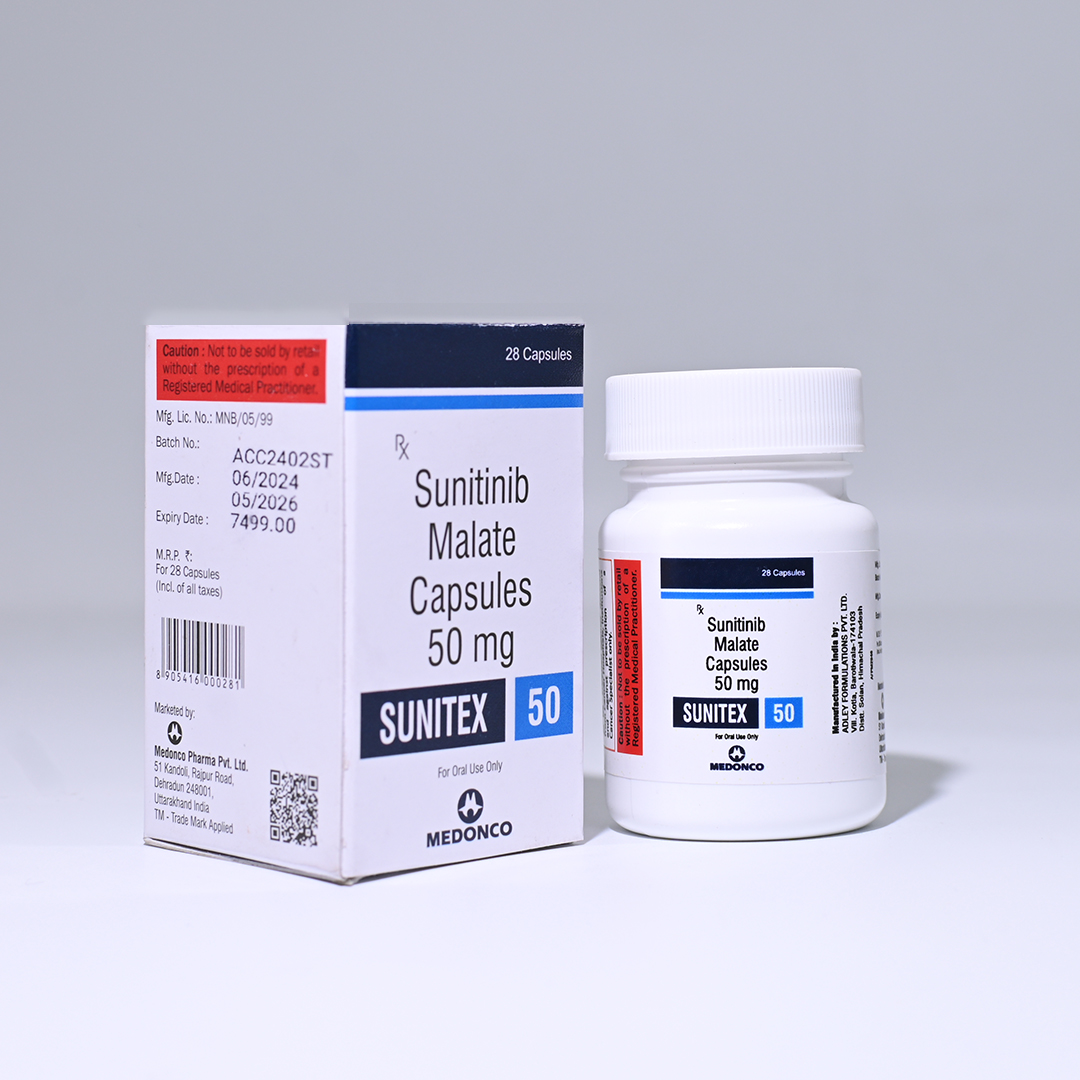







SUNITEX 50MG
Sunitinib Malate 50mg
Net Qty- 28 Capsules
Shelf-Life- 2 Years
Sunitex (Sunitinib Malate 50mg) is an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) used to treat a variety of cancers by targeting pathways essential for tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis.
USE
Sunitinib is FDA-approved for:
Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC):
- First-line treatment for metastatic RCC.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST):
- For patients intolerant to or progressing on imatinib therapy.
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (pNET):
- For progressive, well-differentiated tumors with unresectable or metastatic disease.
Other Off-Label Uses:
- Advanced thyroid cancers and some sarcomas.
Mechanism
of Action
Sunitinib inhibits multiple receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), disrupting tumor growth and angiogenesis:
Angiogenesis Pathways:
- Targets VEGFR (1, 2, 3) and PDGFR-α/β, cutting off blood supply to tumors.
Tumor Proliferation Pathways:
- Inhibits c-KIT, FLT3, RET, and CSF-1R to block tumor growth signals.
This broad activity makes sunitinib effective in cancers dependent on these pathways.
Administration
Standard Dose:
50 mg once daily, orally, on a 4-weeks-on, 2-weeks-off schedule.
Dose Modifications:
Dose adjustments may be needed in 200 mg increments based on patient tolerance.
Administration Instructions:
Take with or without food.
Swallow capsules whole.
Common Side Effects
Frequent (>20%):
- Fatigue and Asthenia:
- Most common; may require dose interruptions or modifications.
- Gastrointestinal (GI):
- Nausea, diarrhea, stomatitis, and anorexia.
- Hand-Foot Syndrome (HFS):
- Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (redness, swelling, and pain in hands/feet).
- Hypertension:
- Onset often within the first treatment cycle; requires regular monitoring.
Hematologic Toxicities:
- Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia.
Liver Toxicity:
- Elevations in ALT, AST, or bilirubin levels.
Severe or Rare Side Effects
Cardiotoxicity:
- Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF) reduction and heart failure have been reported.
- ECG monitoring is recommended in patients with cardiac risk factors.
QT Prolongation:
- Use cautiously with other QT-prolonging medications.
Thyroid Dysfunction:
- Hypothyroidism is common; hyperthyroidism is less frequent.
Severe GI Toxicities:
- Rare perforation or bleeding events.
Proteinuria and Nephrotoxicity:
- Monitor urine protein regularly.
Monitoring and Precautions
Baseline and Periodic Monitoring:
- Blood Pressure:
- Check regularly; manage hypertension proactively.
- Liver Function Tests (LFTs):
- Monitor ALT, AST, bilirubin.
- Thyroid Function Tests:
- Assess at baseline and periodically.
- Ejection Fraction (LVEF):
- Consider for high-risk cardiac patients.
Precautions:
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
- Contraindicated due to teratogenic potential.
- Contraception:
- Recommended during treatment and for at least 4 weeks post-therapy.
Drug Interactions
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors:
- Ketoconazole, erythromycin: Increase sunitinib exposure and toxicity.
- CYP3A4 Inducers:
- Rifampin, phenytoin: Reduce sunitinib levels and efficacy.
- Anticoagulants:
- Monitor for bleeding risk due to interaction with warfarin.
Clinical Effectiveness
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC):
- Demonstrates significant improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) compared to interferon-alpha in metastatic RCC patients.
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST):
- Provides benefits in patients progressing on or intolerant to imatinib.
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (pNET):
- Prolongs PFS and improves symptom control.
Tips for Patients
Adherence:
- Take the medication consistently at the same time each day.
Symptom Monitoring:
- Report fatigue, swelling, or chest pain early.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Stay hydrated and follow a low-salt diet to manage blood pressure.